Mellitus 1 Diabetes
Our patients tell us that the quality of their interactions, our attention to detail and the efficiency of their visits mean health care like they've never experienced. see the stories of satisfied mayo clinic patients. Type 1 diabetes signs and symptoms can appear relatively suddenly and may include: 1. increased thirst 2. frequent urination 3. bed-wetting in children who previously didn't wet the bed during the night 4. extreme hunger 5. unintended weight loss 6. irritability and other mood changes 7. fatigue and weakness 8. blurred vision. Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. mellitus 1 diabetes insulin is a hormone needed to allow sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy. different factors, including genetics and some viruses, may contribute to type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is a disease in which the body does not make enough insulin to control blood sugar levels. type 1 diabetes was previously called insulin-dependent diabetes or juvenile diabetes. during digestion, food is broken down into basic components. carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, primarily glucose. glucose is a critically important source of energy for the body's cells. to provide energy to the cells, glucose needs to leave the blood and get inside the cells. insulin tra Type 1 diabetes makes up an estimated 5–10% of all diabetes cases or 11–22 million worldwide. in 2006 it affected 440,000 children under 14 years of age and was the primary cause of diabetes in those less than 10 years of age. the incidence of type 1 diabetes has been increasing by about 3% per year. rates vary widely by country.
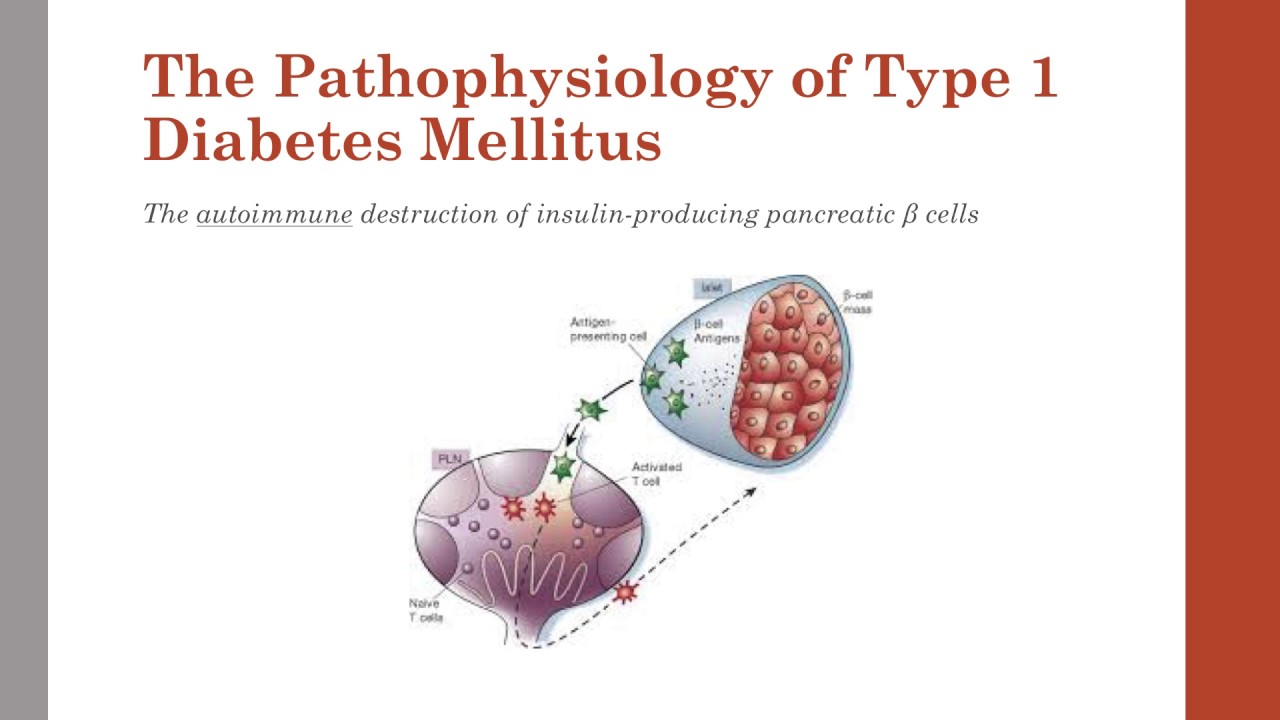
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown. usually, the body's own immune system — which normally fights harmful bacteria and viruses — mistakenly destroys the insulin-producing (islet, or islets of langerhans) cells in the pancreas. other possible causes include: 1. genetics 2. exposure to viruses and other environmental factors. Initial symptoms symptoms usually come on suddenly and strongly. typically the most prominent symptoms are excessive urination and extreme thirst. this is because the increased glucose in the blood causes the kidneys to create more urine than usual. losing more fluid in the urine makes a person dehydrated. and dehydration leads to great thirst. children may start to wet the bed again. weight loss, with no loss of appetite, also is common. the weight loss is due in part to dehydration. water h
Important Tips On How To Find The Best Shoes For Diabetes

Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 Type 2 And Gestational Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms Causes Treatment
Type 1 diabetes is diagnosed by a combination of symptoms, a person's age and blood tests. the blood tests include tests for sugar levels and for other substances. fasting plasma glucose (fpg) test. blood is taken in the morning after fasting overnight. normally, blood sugar levels remain between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl). diabetes is diagnosed if a fasting blood sugar level is 126 mg/dl or higher. oral glucose tolerance test (ogtt). blood sugar is measured two hours after d Over time, type 1 diabetes complications can affect major organs in your body, including heart, blood vessels, nerves, eyes and kidneys. mellitus 1 diabetes maintaining a normal blood sugar level can dramatically reduce the risk of many complications. eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. 1. heart and blood vessel disease. diabetes dramatically increases your risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, s What is type 1 diabetes mellitus? type 1 diabetes is a disease in which the body does not make enough insulin to control blood sugar levels. type 1 diabetes was previously called insulin-dependent diabetes or juvenile diabetes. during digestion, food is broken down into basic components.
Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. insulin is a hormone needed to allow sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy. different factors, including genetics and some viruses, may contribute to type 1 diabetes. although type 1 diabetes usually appears during childhood or adolescence, it can develop in adults. despite active research, type 1 diabetes has no cure. treatment f Diabetes mellitus, also called diabetes, is a term for several conditions involving how your body turns food into energy. when you eat a carbohydrate, your body turns it into a sugar called glucose. See more videos for 1 diabetes mellitus.
More 1 diabetes mellitus images. Diabetes mellitus is a disease that prevents your body from properly using the energy from the food you eat. diabetes occurs in one of the following situations: the pancreas (an organ behind your stomach) produces little insulin or no insulin at all.
See full list on drugs. com. See full list on mayoclinic. org.
There's no known way to prevent type 1 diabetes. but researchers are working on preventing the disease or further destruction of the islet cells mellitus 1 diabetes in people who are newly diagnosed. ask your doctor if you might be eligible for one of these clinical trials, but carefully weigh the risks and benefits of any treatment available in a trial. About diabetes, type 1 type 1 diabetes mellitus, more commonly known as type 1 diabetes, is a disease in which the pancreas produces too little insulin to meet the body's needs. insulin is a hormone that helps control the level of glucose in the blood. glucose is the main form of sugar in the body. No matter how type 1 diabetes has shown up in your life, you can find success by balancing your medications, and sticking to your daily exercise routine and nutrition plan. but wherever you are with this challenge, you can always reach out for help of any kind—from your caregivers, your family or other people who live with type 1 diabetes.
Some known risk factors for type 1 diabetes include: 1. family history. anyone with a parent or sibling with type 1 diabetes has a slightly increased risk of developing the condition. 2. genetics. the presence of certain genes indicates an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes. 3. geography. the incidence of type 1 diabetes tends to increase as you travel away from the equator. 4. age. although type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, it appears at two noticeable peaks. the mellitus 1 diabetes first peak oc Diabetes mellitus refers to a group of diseases that affect how your body uses blood sugar (glucose). glucose is vital to your health because it's an important source of energy for the cells that make up your muscles and tissues. it's also your brain's main source of fuel. the underlying cause of diabetes varies by type.
Comments
Post a Comment